
Do Orthotics Help Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
If you’re dealing with Posterior Tibial Tendonitis (PTT) – also known as Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD), you know how challenging and painful it can be. This condition affects the tendon that supports the arch of the foot (posterior tibial tendon), leading to discomfort and mobility issues. But there’s a practical solution that might help – orthotics.
Do Orthotics Actually Work for Treating Posterior Tibial Tendonitis?
In short, yes. The effectiveness of orthotics in treating posterior tibial tendonitis is widely recognised. By wearing orthotics, sufferers of PTT can experience improved function and take part in daily activities in relative comfort. Various studies indicate a reduction in pain levels, improved function, and success rates of up to 90% in patients with PTTD, with a study by Kulig et al finding that they reduced pain levels and improved functioning in all participants.
Understanding Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Imagine the tendon that runs along the inside of your ankle and down into your foot – that’s your posterior tibial tendon. It plays a big part in holding up your arch and helping you walk. When this tendon gets inflamed or irritated, we call it Posterior Tibial Tendonitis.
Main Causes of PTT
Overuse: This is the most common cause. If you’re doing a lot of walking, running, or activities that put stress on your feet, it can tire out this tendon.
High-Impact Activities: Sports like basketball or tennis, where you’re jumping or changing direction quickly, can put extra strain on the tendon.
Footwear Issues: Shoes that don’t support your arches well enough can add extra stress to this tendon, especially if your foot naturally rolls inward more than usual.
Weight: Carrying more weight puts additional pressure on your feet and this tendon.
Aging: As we get older, our tendons become less flexible and more prone to injury.
Direct Injury: A fall or direct hit to the area can also lead to this condition.
Other Health Conditions: Diabetes and high blood pressure, for example, can affect blood flow and make the tendon more prone to injury.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
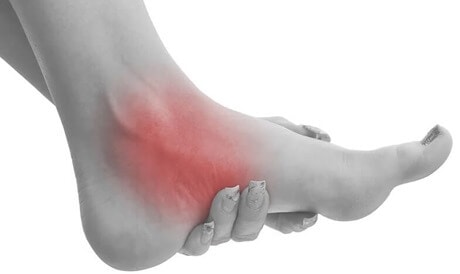
Pain on the Inside of Your Foot and Ankle: This is the most telltale sign. It might start mild and get worse with activity.
Swelling: You might notice some swelling along the inside of your ankle.
Change in Foot Shape: In more advanced cases, the medial arch of your foot might start to look a bit different, like your arch is flattening.
Balance Issues: A common test for this is the single leg heel raise. If you have difficulty or are inable to perform this exercise, it’s a sign you have PTTD.
Difficulty Walking: As it progresses, it might get harder to walk or stand for long periods.
If you’re noticing any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to get it checked out. Catching it early can make a big difference in how quickly and effectively you can manage it. Treatment might include things like rest, ice, better footwear, or custom orthotics to help take the strain off the posterior tibial tendon and give it a chance to heal. Remember, every foot is unique, so what works for one person might be different for another.
To get assessed for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction and other lower limb conditions, call The Lower Limb Clinic today on 03 9532 7455 or book an appointment here.
The Role of Orthotics in Treating Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Let’s talk about how orthotic therapy can help in the treatment of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis. This condition progresses through four stages, each affecting your foot differently. Let’s look at how orthotics work at each stage of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis.
Stage 1 – Inflammation and Mild Pain
At this stage there’s typically some swelling and discomfort of the posterior tibial tendon. You might feel inner foot or ankle pain after activities like running or walking, but there’s no noticeable change in the shape of your foot yet.
Purpose of Orthotics: At this early stage, the main goal is to reduce strain on the tendon to allow it to heal. Orthotics can help by providing proper arch support and reducing overpronation (excessive inward foot rolling).
Type of Orthotics: Over-the-counter orthotics might suffice in this stage, as long as they offer good arch support. Cushioning may also provide comfort.
Stage 2 – Mild Damage and Flat Foot Deformity
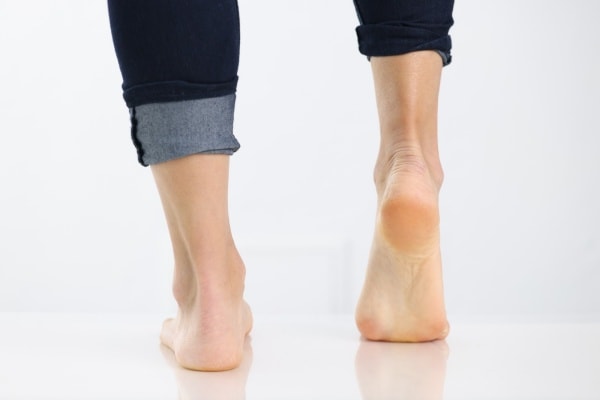
As the condition progresses, the tendon begins to lose its ability to support the arch of the foot. This leads to a slight collapse of the foot’s medial arch. You might start to experience more pain and difficulty in performing activities that put stress on the foot. The foot may also begin to turn outward due to the weakening of the tendon.
Purpose of Orthotics: In this stage, the tendon has started to lose its ability to support the arch, leading to slight foot deformity. Orthotics now need to not only support the arch but also help in correcting foot alignment.
Type of Orthotics: Custom orthotics are generally recommended at this stage. They are tailored to address the specific arch collapse and help realign the foot properly, reducing further strain on the tendon.
Stage 3 – Adult Acquired Flat Foot Deformity and Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
In this more advanced stage, the damage to the tendon is more severe, and the arch of the foot collapses considerably. The foot turns outward even more. This is commonly referred to as adult acquired flat foot deformity or simply flat foot. You’ll likely experience increased pain, balance issues, and have difficulty walking. At this point, the changes in the foot are more significant and may become permanent if not treated.
Purpose of Orthotics: The arch collapse is more pronounced, and the foot may turn outward. Orthotics now play a critical role in providing substantial arch support and preventing further deformation of the foot.
Type of Orthotics: Custom orthotics are essential in this stage. They should be designed to offer robust arch support and possibly include features like heel wedges or deep heel cups to correct foot positioning.
Stage 4 – Severe Deformity and Arthritis
The final stage is characterised by a rigid flatfoot with severe posterior tibial tendon degeneration. The tendon is severely damaged or ruptured, and arthritis often develops in the foot joints due to misalignment and chronic wear and tear. Pain is persistent, and mobility is significantly affected, often requiring more invasive treatments such as surgery.
Purpose of Orthotics: At this advanced stage, the focus shifts to managing pain and preventing further deterioration, as the foot structure might have changed significantly.
Type of Orthotics: Custom made orthotics are crucial and should be designed for maximum support and comfort. They may need to be more rigid to provide stability and might be part of a comprehensive orthopaedic solution that could include braces or specialised footwear.
Why You Should Consider Using Custom Orthotics for PTT Treatment

Custom orthotics are a great choice for treating this condition because they’re tailored specifically for your feet. This personalised fit means they can more effectively correct the changes in your foot caused by PTT, like a collapsing arch or your foot rolling inward. They’re not just for comfort – they’re about supporting your foot in the right way to reduce tendon strain and assist with healing.
These orthotics are also more durable than over-the-counter options. They might cost more upfront, but they last longer, making them a good investment in the long run. Plus, they’re really effective at reducing pain and helping you stay active, which is crucial for managing Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction.
And most importantly, especially in the early stages of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis, they can prevent the condition from getting worse and even remove the condition entirely.
Additional Treatment Options

When dealing with Posterior Tibial Tendonitis, it’s best to take a multi-faceted approach along with using orthotics. First up, rest up and use ice on the sore area for about 15-20 minutes a few times a day to help with the pain and swelling. Physical therapy can be really helpful too; certain exercises strengthens and stretches your foot and ankle muscles which can ease the pain and help you move better.
For pain and swelling, you can use NSAID’s like ibuprofen, but it’s best not to rely on these too much as they only mask the symptoms and don’t actually fix the problem.
If your pain is particularly bad, your doctor might suggest wearing a brace or a special boot to keep your foot from moving too much, giving your tendon a break to heal up. Sometimes, for really tough pain and swelling, corticosteroid injections are an option, but we don’t use them a lot because they could make your tendon weaker over time.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing some can take the pressure off your tendon. It’s also a good idea to change up your activities, especially avoiding stuff that puts a lot of strain on your tendon, like running on rough terrain.
And don’t forget about your shoes – choose supportive shoes that support your arch well and are cushiony. Finally, if none of these things are helping enough and your tendon is really damaged, surgery might be the next step. Everyone’s different, so what helps one person might not be the best for someone else.
Get a Tailored Solution to Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
Ultimately, dealing with PTT is not a one-size-fits-all situation. What works for one person may not work for another. It’s essential to get a professional evaluation to understand your specific needs better.
So if you’ve been struggling with persistent inner foot and ankle pain and think that Posterior Tibial Tendonitis might be the culprit, it’s time to act. Don’t wait until the condition becomes more severe. Early intervention often leads to faster results and less disruption to your life – so you can go back to enjoying your daily activities pain-free.
Get a professional assessment of your lower limb condition with The Lower Limb Clinic today. New patients can get their assessment Gap-Free! But it’s limited to 3 spots per week so book early.
